Metabolics Report
Metabolism encompasses all cellular chemical reactions vital for life, including anabolism (building molecules like sugars and proteins) and catabolism (breaking them down to release energy as ATP). Maintaining a balance between these processes is crucial for healthy energy metabolism and cell function. The Metabolics Report offers insight into how genes shape metabolic differences and influence energy regulation, longevity, and healthspan.
Metabolism encompasses all chemical reactions in cells and is crucial for life. It consists of two main processes: anabolism, which builds substances like sugars and proteins, and catabolism, which breaks them down to release energy in the form of ATP. Maintaining a balance between these processes is essential for energy metabolism and healthy cell function.
The Metabolics report details genes that significantly influence key metabolic pathways, featuring over 40 genes and 50 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) across six areas: appetite regulation, nutrient sensing, sugar and fat metabolism, cholesterol and bile production, mitochondrial function, and inflammation.
Genes Included:
Appetite Regulation: BDNF, FAAH, FTO, LEPR, MC4R, NPY, POMC
Nutrient Sensing: ADIPOQ, FOXO3, HIF1A, IRS1, PARP1, PGC1A, PPARA, PPARG, SIRT1, VEGFA
Sugar Metabolism: AMPD1, GCK, GLUT2, IRS1, PPARG, TCF7L2
Fat Metabolism: ADRB3, CD36, CPT1A, FABP2, LPL, PLIN1, PPARA, SREBF1
Cholesterol/Bile: CYP7A1, HMGCR, LDLR, SREBF1
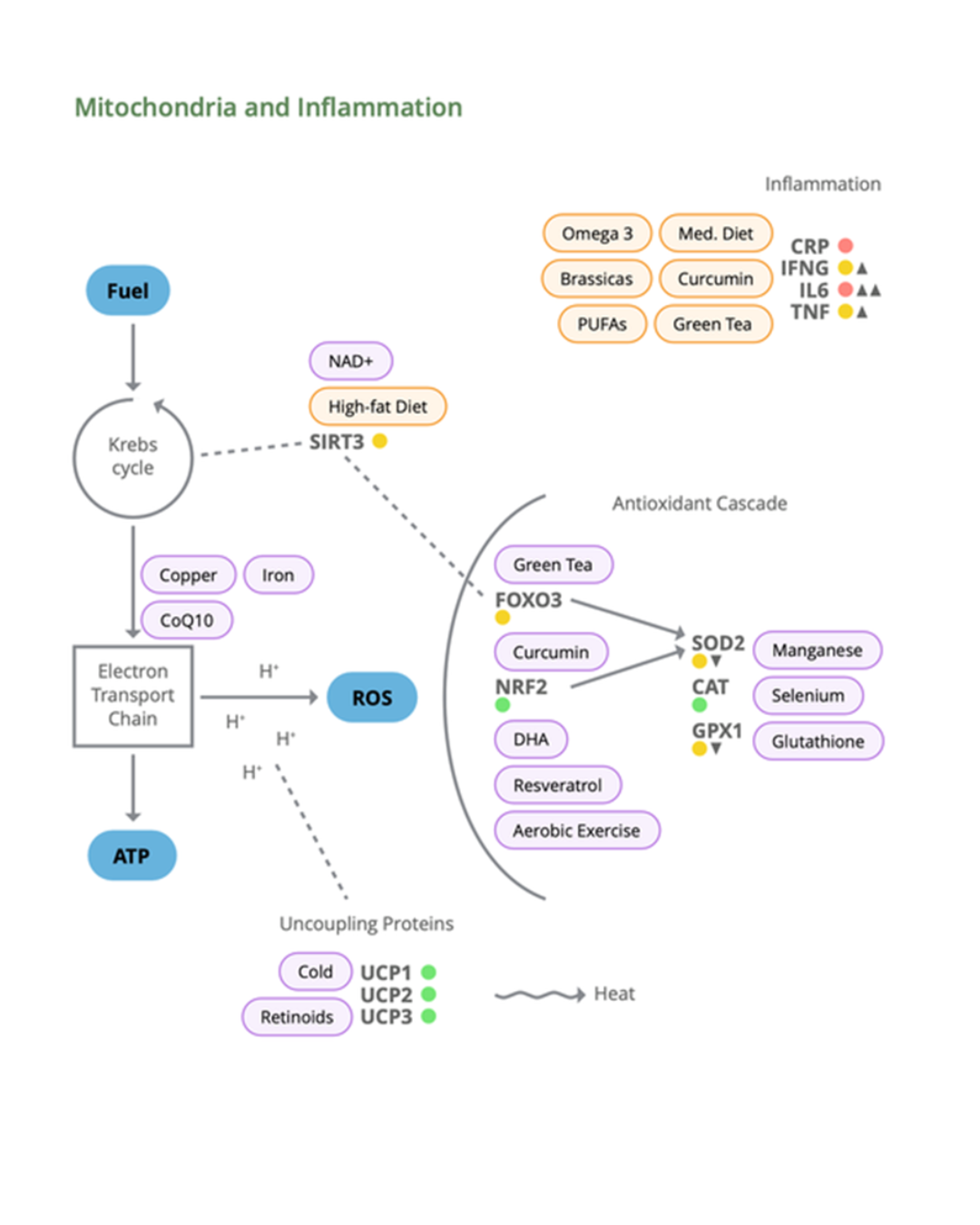
Mitochondria/Inflammation: CAT, CRP, FOXO3, GPX1, IFNG, IL6, NRF2, SIRT3, SOD2, TNF, UCP1/2/3
Lifecode Gx® reports feature:
Personalised, colour-coded genotype results
Clear gene function and SNP impact summaries
Clinically relevant SNPs
Nutrient and epigenetic insights
Research evidence link